The First Seismometer
To measure which direction an earthquake came from, the Ancient Chinese invented the seismometer. The base was six feet in diameter and was constructed of copper. Eight dragon heads and eight toads with their mouths open were positioned at 45o angles from the next head to represent the eight directions. In each dragon head was a lead ball, and this was dropped when the earth's tectonic plates had a movement. The scholars could then decide in which direction the earthquake was. Inside the kettle was a pendulum which was connected to levers which would open the dragon mouths when it was swung by the crust's movements. This was how they determined how to solve where the earthquakes came from when it was invented in between the years 78-139 AD.
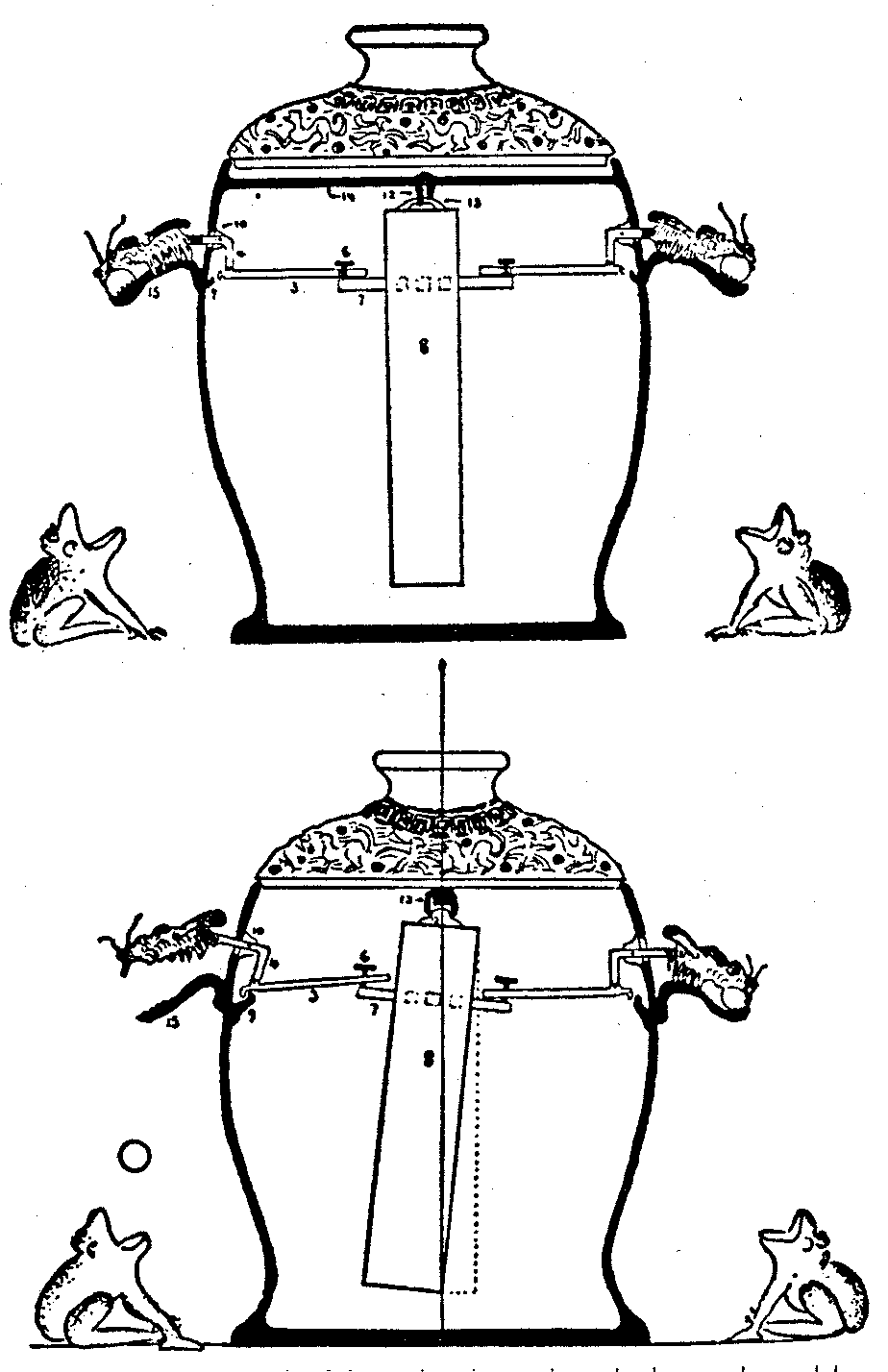
Taken from pg. 81 of Columbus Was Chinese.
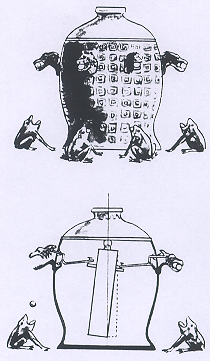
Taken from pg. 97 of Wonders of Ancient Chinese Science.
Go back to the Chinese Inventions page.


